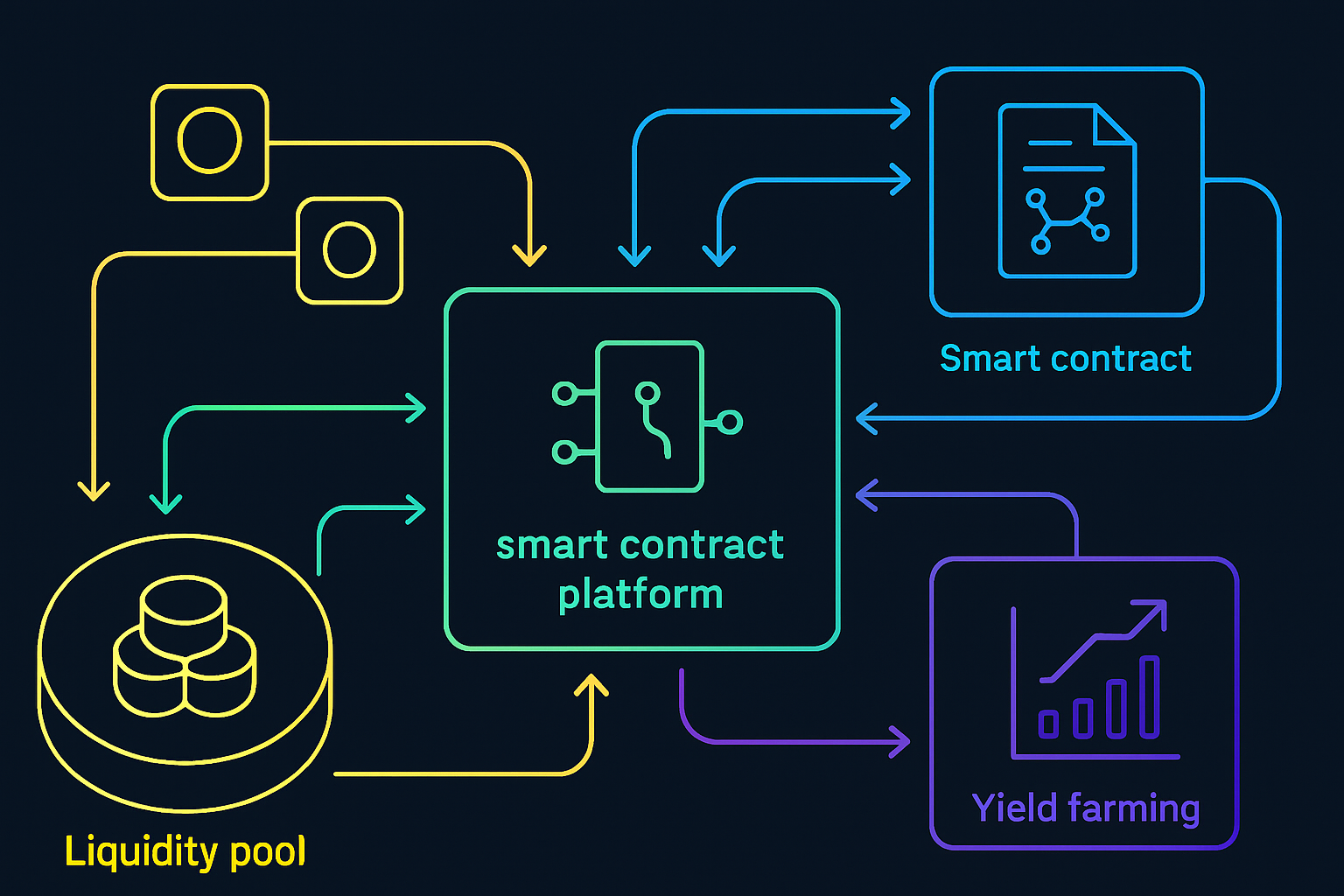
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has transformed the way we interact with money, removing intermediaries and relying on smart contracts to automate everything from lending to liquidity provision. But with this innovation comes a new set of risks: hidden vulnerabilities in code, economic exploits, and the potential for catastrophic protocol failures. As the DeFi ecosystem continues to grow, understanding these risks is not just prudent, it’s essential for anyone looking to safeguard their digital assets.

Hidden Vulnerabilities: How Smart Contract Flaws Threaten DeFi
Smart contracts are only as secure as the code they’re written in. Even minor errors can open the door to devastating attacks. Let’s break down the most common vulnerabilities:
- Reentrancy Attacks: These occur when a contract allows an external call to another contract before updating its own state. The infamous DAO hack in 2016, which resulted in a $60 million loss, was a textbook example. Attackers repeatedly called back into the contract, draining funds before balances could update.
- Flash Loan Exploits: Flash loans let users borrow enormous sums with no collateral, provided the loan is repaid in the same transaction. Attackers use this tool to manipulate protocol logic or price feeds, as seen in the Harvest Finance exploit that led to $24 million in losses.
- Oracle Manipulation: Many DeFi protocols depend on oracles for external data like prices. If an oracle is compromised, attackers can feed false information to smart contracts, as happened with Baby Doge’s $137,000 loss in May 2023. For a deeper dive into how these vulnerabilities can trigger protocol failures, see this guide.
- Integer Overflow/Underflow: When arithmetic operations exceed the maximum or minimum value a variable can hold, attackers can exploit this to mint tokens or drain funds. The BeautyChain token flaw is a prime example.
- Front-Running Attacks: By monitoring the mempool for pending transactions and paying higher fees, bots can jump ahead of legitimate trades, profiting at the expense of regular users.
- Access Control Vulnerabilities: Misconfigured permissions can allow unauthorized actors to execute sensitive functions. The Poly Network hack, which saw $600 million stolen, was rooted in logic errors and permissions flaws. Learn more about how access control issues lead to exploits here.
“With billions of dollars locked in DeFi protocols, a single overlooked bug can erase years of innovation overnight. “
Economic Exploits: Beyond Bugs and Into Game Theory
Not all DeFi risks are technical. Many stem from economic design flaws and market dynamics that can be just as destructive as code vulnerabilities:
- Impermanent Loss: Liquidity providers on Automated Market Makers (AMMs) like Uniswap often face impermanent loss, a reduction in value compared to simply holding assets, especially when prices diverge. In Uniswap v3, nearly half of LPs lost money due to impermanent loss outpacing fee earnings.
- Liquidation Spirals: Over-leveraged positions can create feedback loops during volatile markets. MakerDAO’s “Black Thursday” event saw $8 million in ETH sold for zero due to auction failures and cascading liquidations.
- Economic Design Flaws: Unsustainable tokenomics or incentive structures can destabilize a protocol. Olympus DAO’s high APY model is a cautionary tale of how economic missteps can lead to rapid collapse.
Mitigation Strategies: Hedging Against Smart Contract and Economic Risk
Given the complexity and interconnectedness of DeFi protocols, risk mitigation requires a multi-layered approach. Here are some of the most effective strategies employed by leading projects and investors:
- Thorough Audits: Before launch, reputable security firms rigorously audit smart contracts. Despite this, even audited contracts can be exploited due to overlooked logic errors or new attack vectors. For a detailed look at why this happens, check out this analysis.
- Formal Verification: Mathematical proofs are used to ensure contracts behave as intended under all possible scenarios. Cardano and other projects have set new standards here.
- Bug Bounties and Community Oversight: Platforms like Immunefi incentivize ethical hackers to find vulnerabilities before malicious actors do.
- Decentralized Oracles and Multi-Signature Wallets: Using multiple independent oracles and requiring several approvals for critical actions helps reduce single points of failure.
- Insurance Protocols: Decentralized insurance platforms such as Nexus Mutual have paid out over $17 million in claims since inception, providing a crucial safety net for users facing smart contract failures or exploits. To learn how smart contract exploit insurance works, see this guide.
The evolving nature of DeFi means new risks are constantly emerging. Staying informed and proactive is the best defense against both technical and economic threats.
While robust technical defenses are crucial, true risk management in DeFi also means knowing when to hedge and how to diversify exposure. Even the most secure protocols can fall victim to unforeseen exploits or cascading failures triggered by interconnected markets. That’s why more sophisticated investors are turning to layered hedging strategies and on-chain insurance products, not just as a last resort, but as a core part of their portfolio design.
Proactive Hedging: Tools for Modern DeFi Investors
Hedging in DeFi extends beyond simply spreading assets across multiple protocols. It involves:
- Protocol Risk Assessment: Before allocating capital, investors should analyze protocol track records, audit histories, and governance structures. Resources like this guide provide frameworks for evaluating protocol robustness before exposure.
- Stablecoin Depeg Protection: With stablecoin depeg events still fresh in market memory, users now have access to derivatives and coverage products designed specifically to hedge against sudden price drops below $1. These tools can be critical during volatile market conditions or systemic stress.
- Diversification Across Chains and Apps: Spreading risk across multiple blockchains and application types helps insulate portfolios from cross-chain vulnerabilities. However, as centralized bridges accounted for 35% of DeFi losses in 2025, it’s essential to understand bridging risks, see this resource.
- Insurance Layering: Combining different insurance protocols (for example, pairing Nexus Mutual with protocol-specific coverage) can enhance protection against both smart contract bugs and economic exploits.
Staying Ahead: Education and Community Vigilance
The landscape of smart contract risk in DeFi is dynamic, what was considered secure yesterday may become tomorrow’s attack vector. Continuous education is vital. Investors should follow security researchers, participate in community calls, and stay updated on new exploits as they emerge.
Communities that foster open reporting of vulnerabilities, rewarding white-hat disclosures rather than punishing them, tend to fare better over the long term. Platforms that prioritize transparency build trust even when incidents occur.
The Path Forward: Building Resilience Into Your DeFi Strategy
No single solution eliminates all smart contract or economic risks in DeFi. The most resilient portfolios combine technical best practices with proactive hedging, diversified exposure, insurance coverage, and ongoing vigilance. As decentralized finance matures, expect more sophisticated risk mitigation tools to emerge, empowering users at every level to participate safely.
If you’re serious about protecting your digital assets from hidden vulnerabilities or economic exploits, make risk management a core pillar of your strategy, not an afterthought. The future belongs to those who prepare for uncertainty while embracing innovation responsibly.